MapReduce is a processing technique and a programming model for distributed computing to deploy and process big data. Hadoop MapReduce is a data processing framework of Hadoop built on the idea of MapReduce, now when we talk about MapReduce we will immediately think of Hadoop MapReduce, so in this article I would like to briefly talk about some places. Hadoop MapReduce is MapReduce.
To better understand the idea of MapReduce, you can review my previous article about MapReduce programming model for Bigdata.
Hadoop MapReduce components
When programming with MapReduce, you only need to pay attention to the following 3 layers:
- Mapper
- Shuffle and sorting
- Reducer
Tổng quan thực thi
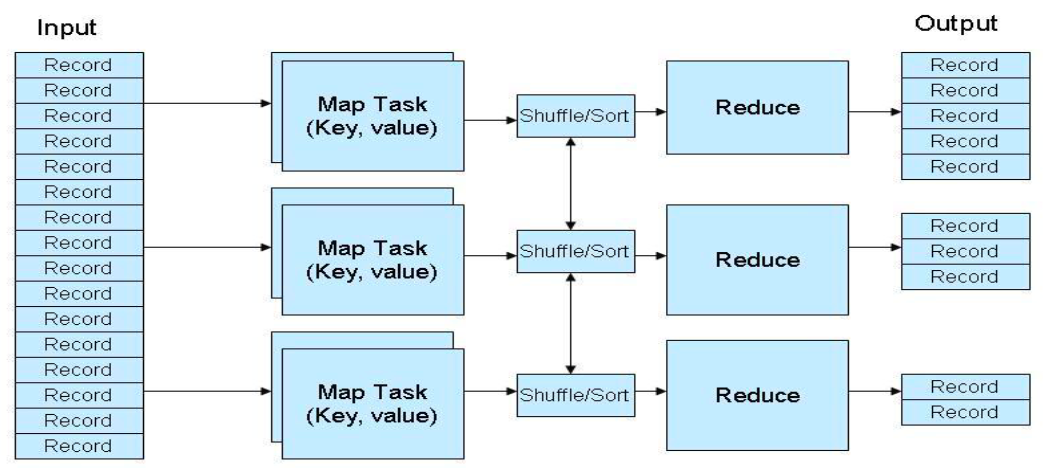
The master machine distributes M
Maptasks to the incoming machines to monitor their progressTasks
Mapread data and perform processing, the results are stored in the local bufferThe
Shufflephase assigns reducers to memory buffers where they are read remotely and processed by reducersReducerexport the results and store on HDFS
Mapper
This is the first phase of the program. There are two steps in this phase: splitting and mapping. A data set is divided into equal units called chunks in the splitting step. Hadoop includes a RecordReader that uses TextInputFormat to convert input decompositions into key-value pairs.
Shuffle
This is the second phase that takes place after completing Mapper. It includes two main steps: sorting and merging. In this phase, key-value pairs are sorted using keys. Merging ensures that key-value pairs are combined.
Reduce
In the Reduce phase, the output of the Shuffle phase is used as input. The Reducer processes this input further to reduce the intermediate values to smaller values. It provides a summary of the entire data set, for example calculating the sum, finding max, min, etc. The output of this phase is stored in HDFS.
Advantages of Hadoop MapReduce
Supports parallel processing and computing (Parallel Processing)
In MapReduce, work is divided among multiple nodes, and each node works on a portion of the work simultaneously. The MapReduce model allows a job to be divided into smaller, completely separate jobs.
Data Locality
Even though the machines are combined into a cluster, as the data grows larger, moving data between machines is very time-consuming and can cause problems such as transmission congestion.
Hadoop overcomes the above problem by distributing data across multiple nodes and each node processes its own pieces of data.
Scalability
Hadoop is highly scalable, can reach thousands of nodes without affecting performance or generating errors.
For example, to scan 1000TB of data on 1 node at a speed of 100MB/s will take 24 days, and when expanding the cluster to 1000 nodes, it will take the equivalent of 35 minutes to scan this 1000TB of data (perfect performance). is not degraded and no errors arise during the expansion process)
Availability & Fault Tolerance
Hadoop stores copies of data on different nodes, so in case of failure the data copy is available whenever required to ensure data availability.
Thanks to the data availability feature, Hadoop has high fault tolerance. When a Task is killed or a node loses connection, leading to that Task not being completed, Hadoop will quickly detect and assign a node. new file containing a copy of that Task’s execution data (ensuring locality )
Low cost (Cost-effective)
Hadoop runs on machines with common hardware, which are cheap machines with low bandwidth. Hadoop is highly fault tolerant so fewer administrators are needed. Hadoop is easy to learn and use, so it also costs little in training and hiring workers.
Security & Authentication
The MapReduce programming model addresses security risks by working with highly confidential HDFS and HBase allowing only approved users to operate on data stored in the system.
Simple programming model
You can see that the MapReduce programming model is extremely simple, in addition, Hadoop MapReduce uses the Java language which is a popular and easy to learn language.
WordCount program with MapReduce
The WordCount program is the classic program that illustrates MapReduce and is used as an example in most introductions to MapReduce.
In this section, I will guide everyone to run this Job with Hadoop MapReduce. The entire source code of the WordCount program can be downloaded HERE.
Step 1: Download Project
Please clone your prepared project to your computer HERE.
Step 2: Install mvn
If your device doesn’t have it mvn, please download it mvn, the installation is very simple so I won’t mention it here.
To check if the installation was successful mvn, use the command mvn --version:
Step 3: Build file jar
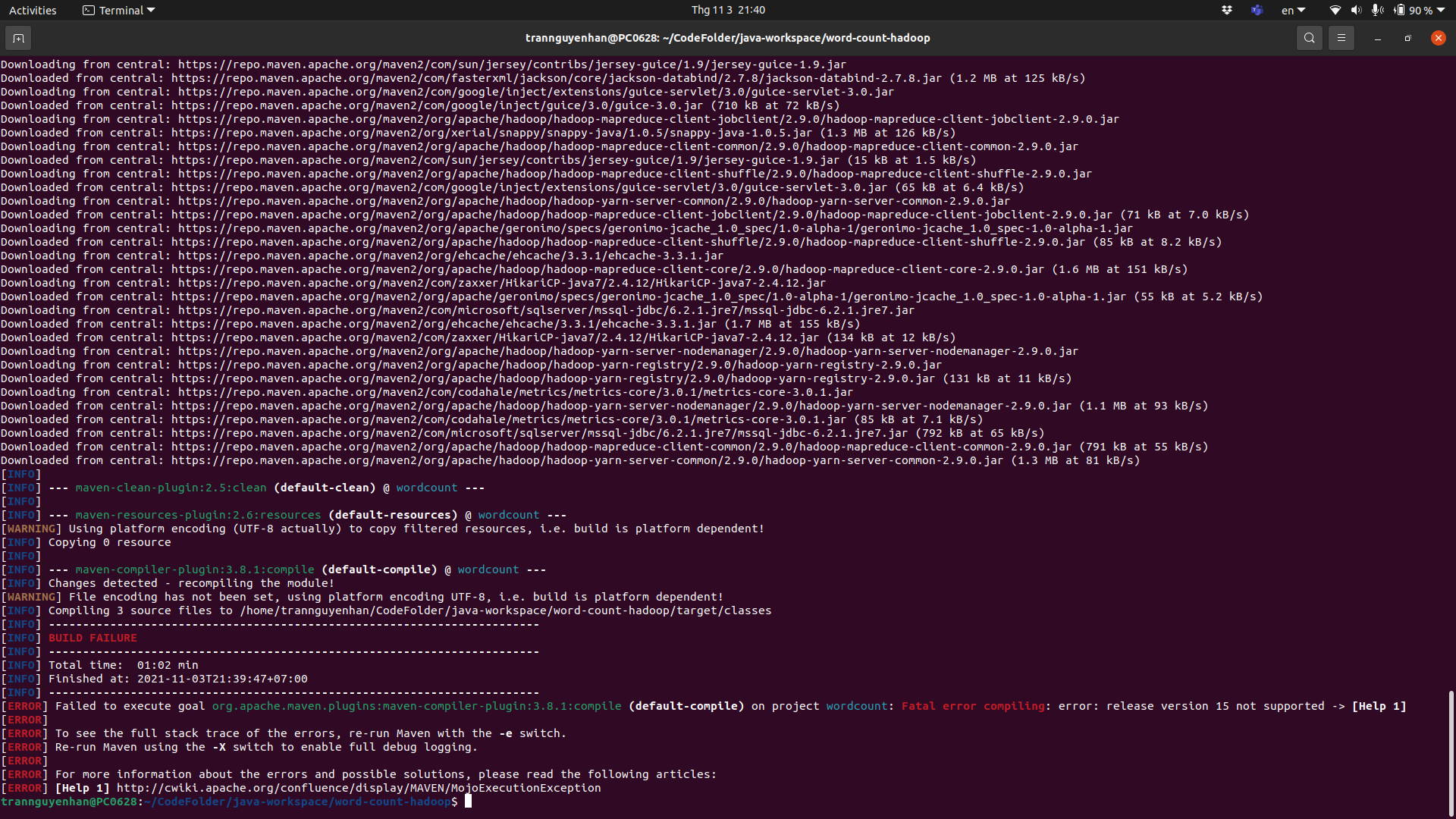
Move to the folder containing the cloned project, run the command mvn clean package to build the project into one file jar (when building for the first time, mvn will have to download the dependencies so it will take a long time, next time it will be faster).
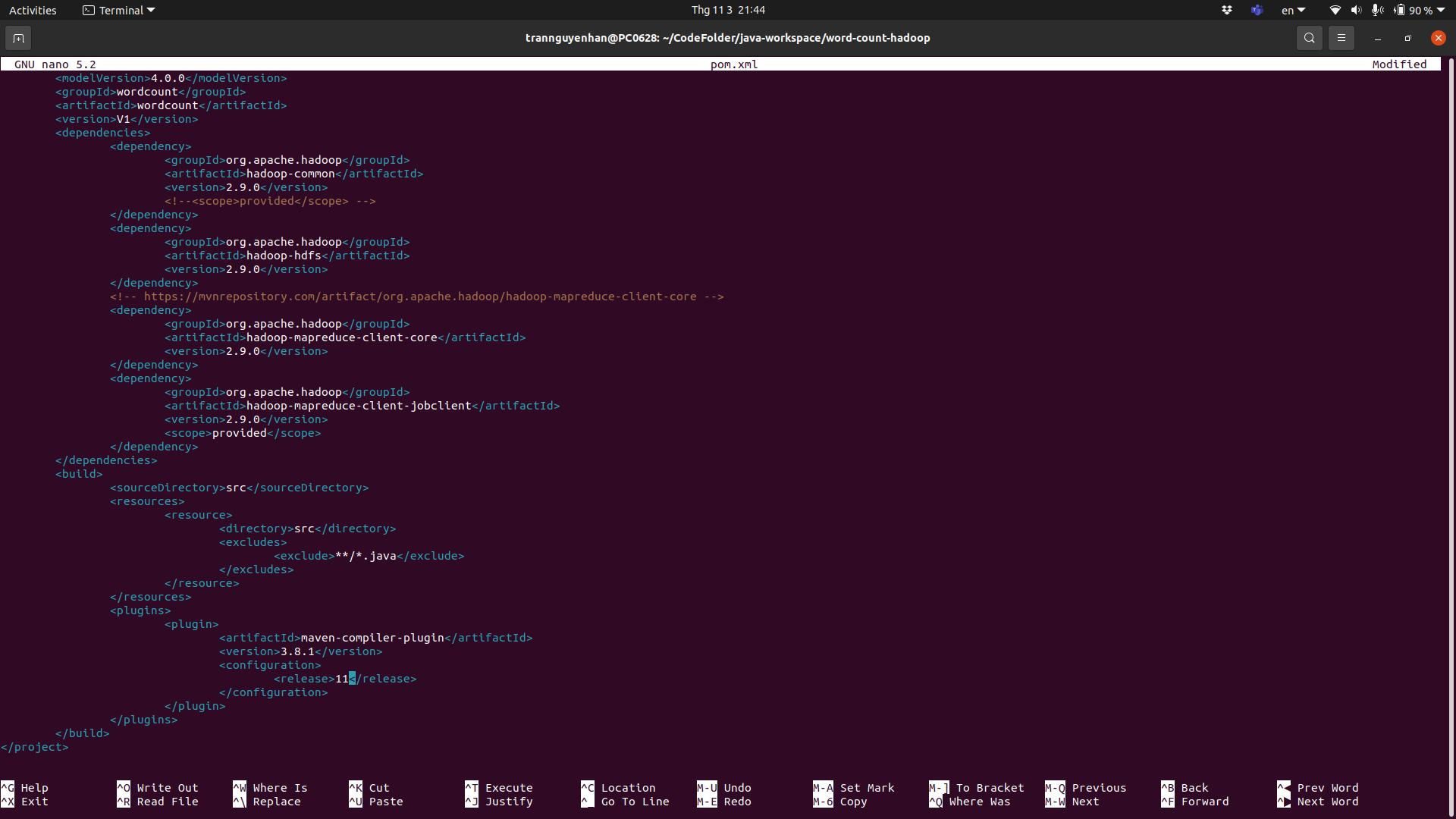
Note that if you get an error like below when building, please correct the jdk version you are using on your computer, for example, the pom configured file is jdk 15, however on my computer there is only jdk 11, then after build it will show the error:
At the file pom.xml in the <plugins> edit tab <release>, it is 11, then save and re-execute the command mvn clean package:
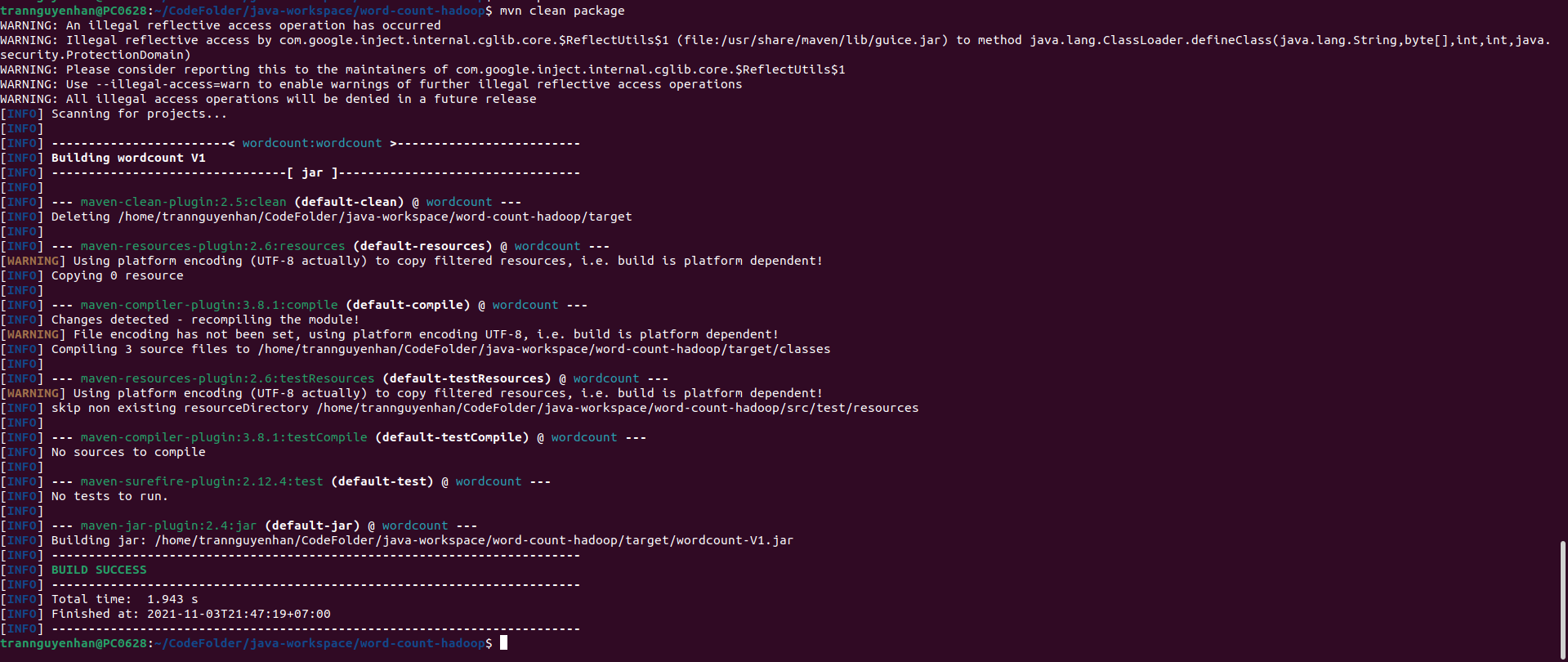
If the text “BUILD SUCCESS” appears, you have successfully built the file jar, the generated file is in the project jar directory . target you can see that this second rebuild is very fast because the dependencies have been downloaded to the local machine.
Step 4: Prepare data
After we have the jar next file, we will prepare the input data, you can take any text file to test, you can run Hadoop with the input located locally, but this only succeeds. If you run a single node and if you have a Hadoop cluster and want to run a job on it, your input file must be pushed to HDFS.
Copy your files from local to HDFS via command line:
1
hdfs dfs -copyFromLocal input.txt /
Review commands to manipulate files and folders on HDFS HERE
Check if input.txt your file is already on HDFS with the command:
1
hdfs dfs -ls /
Step 4: Run the program
Everything is done now, submit your job to Hadoop and wait for the results, run the following command:
1
hadoop jar target/wordcount-V1.jar com.hadoop.mapreduce.WordCount hdfs://localhost:9000/input.txt hdfs://localhost:9000/output
The first parameter
hdfs://localhost:9000/input.txtis the path to the input file. Because the input file is located on HDFS, the path must be addedhdfs://otherwise the program will understand it as a local path.The second parameter
hdfs://localhost:9001/outputis the path to set the program’s output, we will also save the output on HDFSIf you do not install HDFS at the gateway,
9000please correct itIf you submit the job to a multi-node cluster, change it
localhostto the name corresponding to the master machine
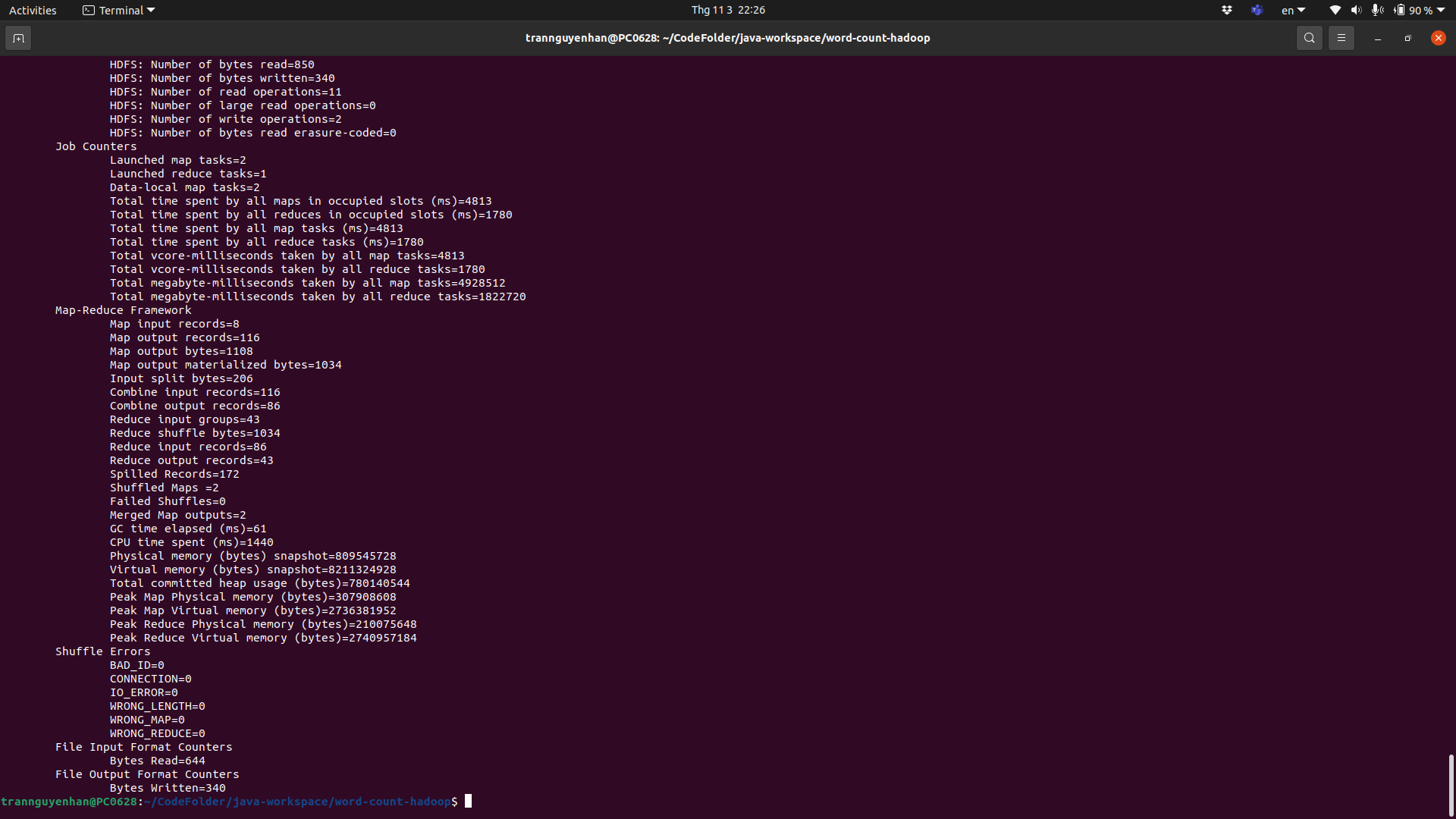
After running, the terminal will display some information about your run job:
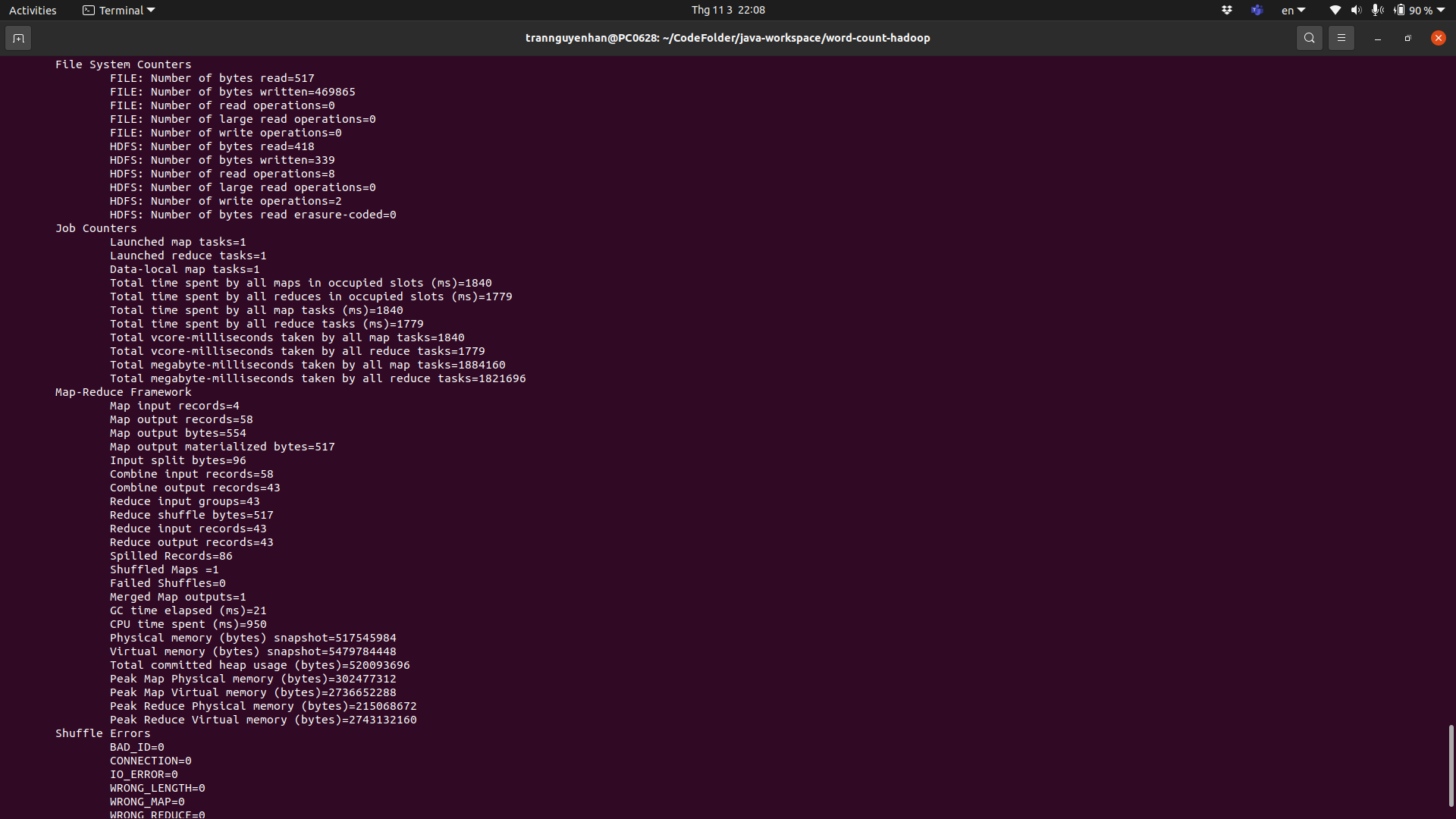
For example, in my job there is 1 Map task and 1 Reduce task, the input file is 332 bytes and the output file is 330 bytes.
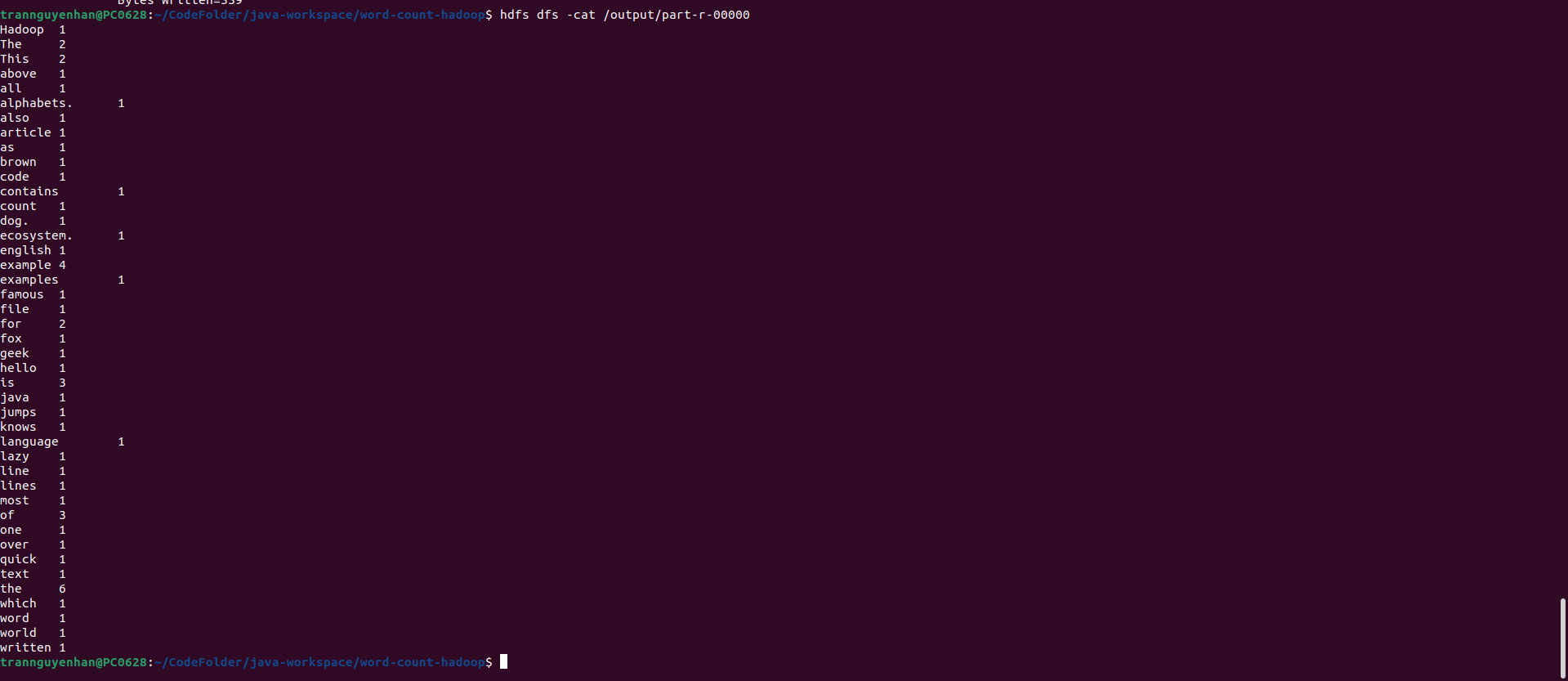
Check the output file output on HDFS via command hdfs dfs -cat /output/part-r-00000:
Run the program with 2 or more Mapper
We cannot set the number of Mapper to run in a job, we can only set the maximum number of Mapper, Hadoop will automatically assign the number of Mapper based on the number of blocks.
For Hadoop to run with 2 Mapper, the input data must be stored on 2 blocks by HDFS, so there are 2 ways:
One is that your input file is heavier than the block size, then HDFS will store that file as 2 blocks.
Second, replace your input with a folder and in that folder you put any 2 text files. Hadoop allows data input to be a folder and it will automatically scan all files in that folder.
Now I will create a copy of the input.txt previous file and name it input-1.txt:
1
hdfs dfs -cp /input.txt /input-1.txt
Then create a directory input on HDFS:
1
hdfs dfs -mkdir /input
Move each file in turn input.txt and input-1.txt into the folder input:
1
2
hdfs dfs -mv /input.txt /input
hdfs dfs -mv /input-1.txt /input
Check if the data is in the folder input or not:
1
hdfs dfs -ls /input
So the data is done, now we run the program again:
1
hadoop jar target/wordcount-V1.jar com.hadoop.mapreduce.WordCount hdfs://localhost:9000/input hdfs://localhost:9000/output
- Now our input is not a file
input.txtanymore but a folderinput, so let’s change the input parameter
After the program ends, we can immediately see that the information about the program has changed, such as the number of Map tasks that have been run is 2:
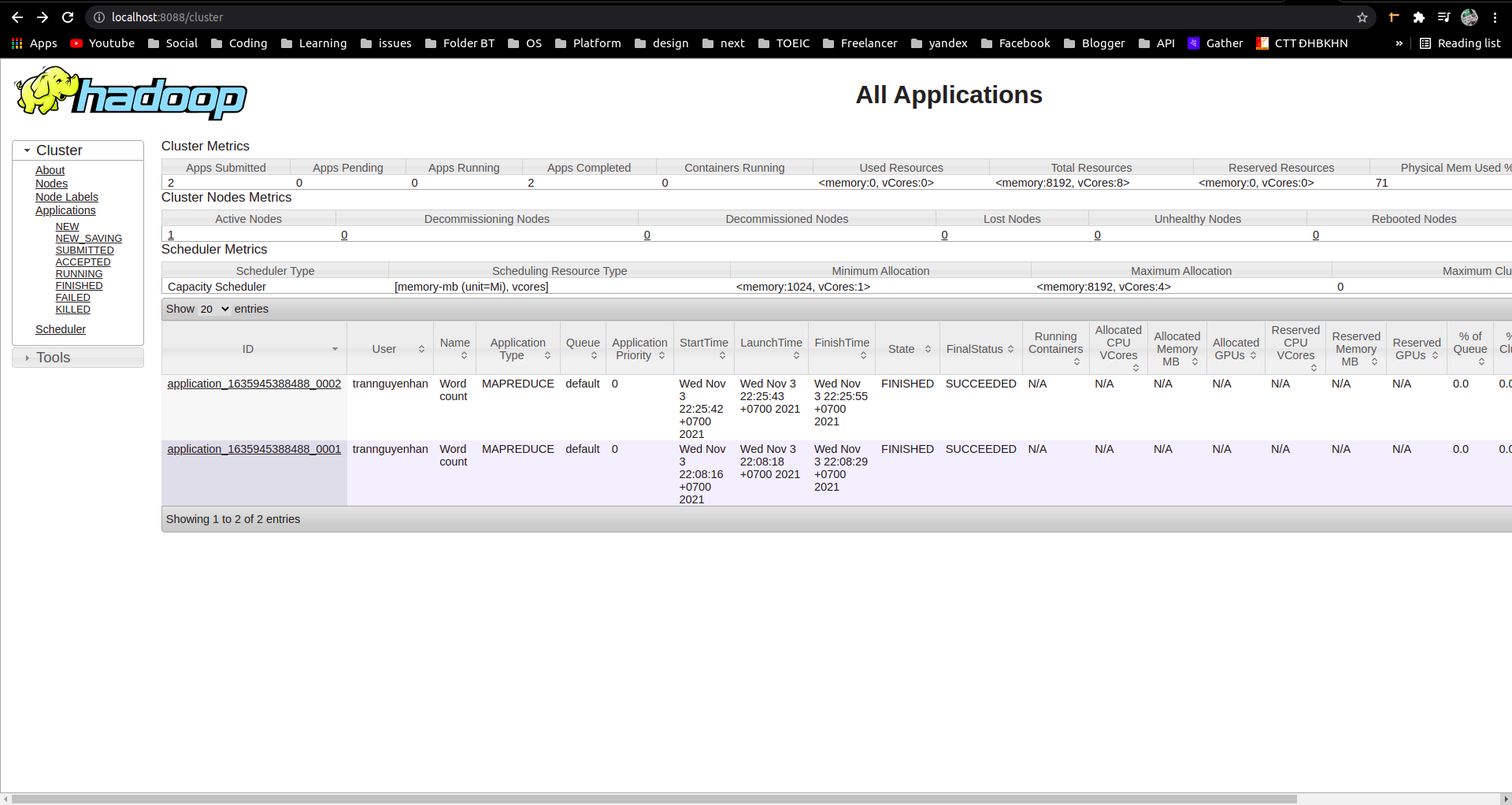
Check the run job information at YARN’s UI portal
To be more vivid, you can check the information of a job that has been run at YARN’s UI port, port 8088:
1
http://localhost:8088/cluster
If you run the job on a multi-node cluster, change
localhostthe name to correspond to the master machine
- Above shows information about the 2 WordCount jobs that I just ran
- Click on each task one by one to view detailed information about that task
Reference: https://hadoop.apache.org, https://www.educba.com/, https://www.edureka.co/